Stages of Wound Healing - A wound is a break or a cut in the skin. It can happen for many reasons, including an injury, surgery, or infection. Wounds can be minor, like a scrape, or more serious, like a deep cut. In the process of healing, new skin grows to replace the damaged area. This skin replacement happens during the wound healing process.

- Abrasions occur when the top layer of skin gets scraped off. Abrasions are also called grazes.
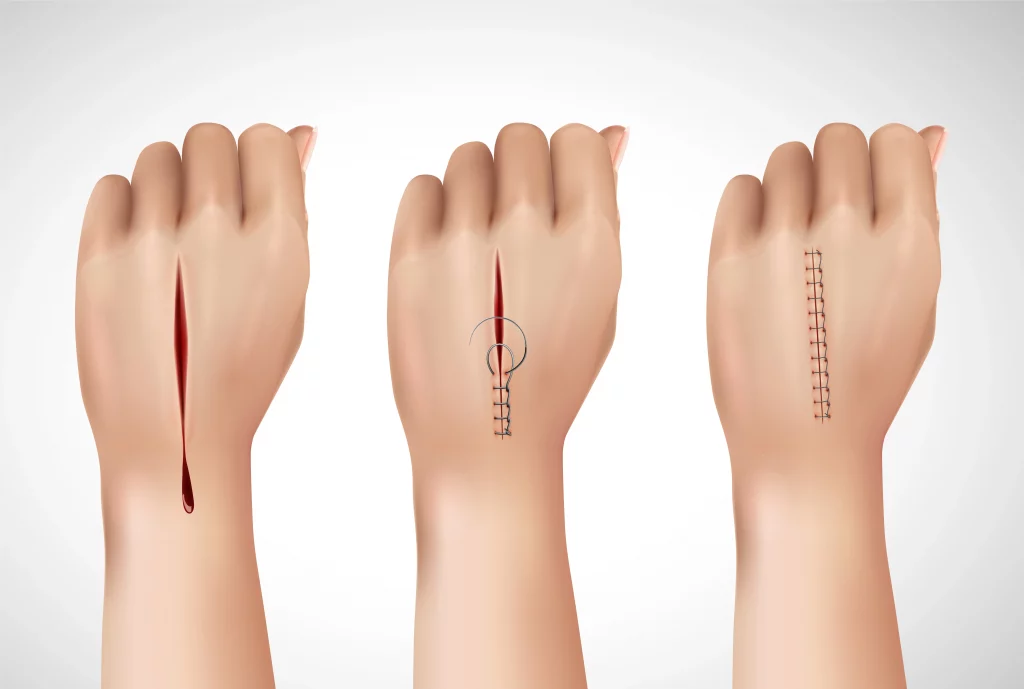
- Lacerations are deep cuts that go through the skin and sometimes into the underlying tissues.
- Punctures occur when something sharp penetrates the skin, such as a nail or splinter.
Most wounds go through the process of healing independently, but some may require medical treatment. Treatment will depend on the type of wound and how severe it is.
- Abrasions usually heal within a few days and do not require medical treatment. A person can clean the wound with soap and water and cover it with a bandage if needed.
- Lacerations may require stitches to close the wound. The wound will be cleaned and repaired with stitches, staples, or skin adhesive. This repair will help accelerate the scar healing stages.
- Punctures may also require medical treatment. The object that punctured the skin will need to get removed, and the wound will require cleaning. A person may also need a tetanus shot if they have not had one in the last five years.
The wound healing process happens in three stages:
- The inflammatory stage
- The proliferative stage
- The maturation and remodeling stage
The inflammatory stage is one of the first stages of wound healing. It begins at the time of injury and lasts about 3 to 5 days. This stage is crucial because it helps to protect the wound from infection. Scar healing stages are essential for the recuperating body.
During this stage, blood vessels constrict to limit bleeding. White blood cells move to the area to fight infection. Fluid and plasma leak out of the blood vessels and into the wound. This fluid helps to clean the wound and remove debris. As the fluid leaks out, it forms a scab on the surface of the injury.
The proliferative stage is the second stage of wound healing. It begins 3 to 5 days after the injury and lasts about 2 to 3 weeks. During this stage, new blood vessels grow in the area. This process is called angiogenesis. New cells also begin to grow and multiply. These cells form granulation tissue, which fills in the wound. The granulation tissue comprises collagen fibers, fibroblasts, and new blood vessels.
As the granulation tissue grows, it forms a barrier that protects the wound from infection. It also helps to close the wound.
The maturation and remodeling stage is the final stage of wound healing. It begins 2 to 3 weeks after the injury and can last for months or even years. During this stage, the collagen fibers in the granulation tissue begin to align and become stronger. The wound also begins to shrink.
As the wound heals, new skin grows to replace the damaged area. This new skin is not as strong or durable as the original skin.
Wound healing is a complex process that takes time. It is vital to clean wounds and protect them from infection.
A person with a minor wound can treat it at home. Home treatment includes cleaning the wound and protecting it from infection.
To clean a wound:
- Gently wash the wound with soap and water. Do not scrub the wound.
- Apply an antibiotic ointment to the wound if available.
- Cover the wound with a bandage or dressing.
Change the dressing regularly to keep the wound clean and dry. If the dressing gets wet, replace it as soon as possible.
See a doctor if the wound is more than 1/2 inch deep, if bone or tendon is exposed, or if someone cannot close the wound with adhesive strips or butterfly closures. They should also see a doctor if the edges of the wound are gaping or the injury is on the face.
A person with a more severe wound will need to see a doctor. The doctor will clean the wound and may close it with stitches, staples, or skin adhesive. The doctor will also give the person a tetanus shot if needed.