What is Keratin? Keratin is a structural protein that makes up most of your hair, skin, and nails. It's what gives these tissues their strength and flexibility. Keratin also helps protect your cells from damage. Keratin is produced by keratinocytes, the dominant type of cell in the epidermis (the outermost layer of your skin). These cells constantly undergo a process of keratinization, in which they produce keratin fibers that help to hold the skin together.
Keratinocytes are also responsible for producing keratohyalin, a substance that helps form the stiff, waterproof barrier that protects your skin from environmental damage. Keratin is also in other tissues in your body, including your eyes, teeth, and muscles. It's an essential component of these tissues and helps keep them healthy.
Keratin has several benefits for your hair, skin, and nails.
Keratin can help to:
- protect your cells from damage
- keep your skin healthy
- keep your hair strong and resilient
- prevent nail breakage
Keratin may also have some anti-aging properties. Keratin on the skin helps improve elasticity and reduce the appearance of wrinkles. Keratin may also help to protect your skin from damage caused by ultraviolet (UV) rays from the sun.
Keratin supplements are available in various forms, including capsules, creams, and shampoos. You can also get keratin treatments at some salons. These treatments typically involve applying a keratin-based product to your hair and then using heat to seal it.
While keratin supplements are generally safe, they can cause some side effects. These include stomach upset, diarrhea, and headache. Keratin treatments may also cause scalp irritation and allergic reactions in some people. If you're considering taking a supplement or getting treatment, talk to your doctor first to ensure it's right.
Keratin can be used in various ways, depending on your needs.
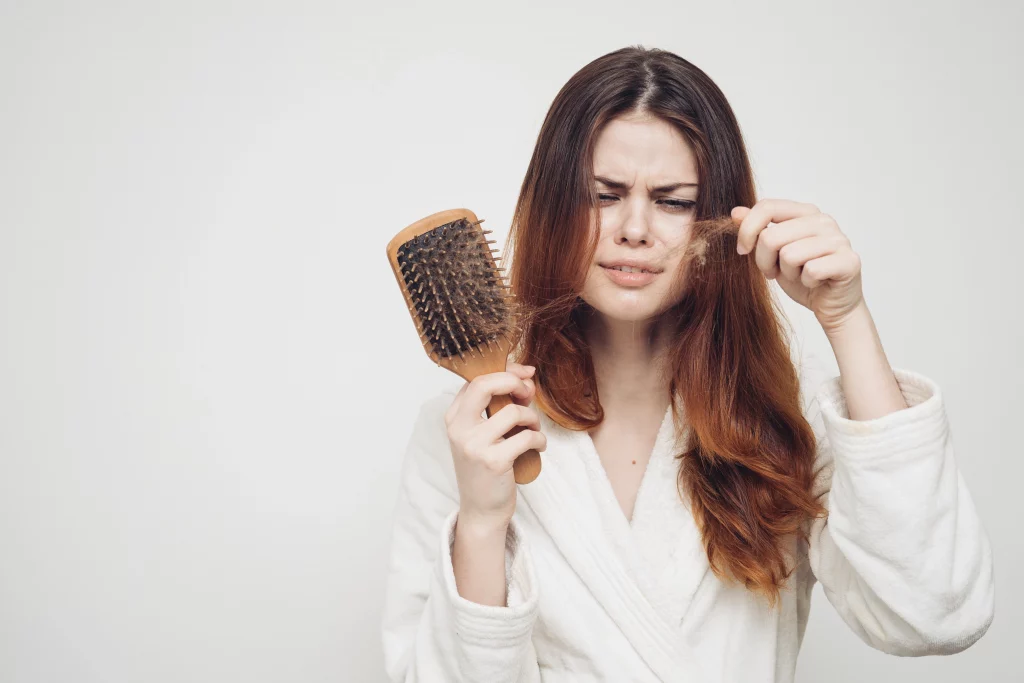

Keratin is vital for healthy hair, skin, and nails. A Keratin deficiency can lead to several problems, including:
Hair loss: Keratin helps to give your hair its strength. A Keratin deficiency can cause your hair to become brittle and break easily. This brittleness can lead to hair loss.
Dry, dull hair: Keratin helps to keep your hair hydrated and looking shiny. A Keratin deficiency can cause your hair to become dry and dull.
Split ends: Keratin helps to prevent split ends. A Keratin deficiency can cause split ends and other damage to your hair.
Brittle nails: Keratin helps to give your nails their strength. A Keratin deficiency can cause your nails to become brittle and break easily.
Dry, scaly skin: Keratin helps to keep your skin hydrated. A Keratin deficiency can cause your skin to become dry and scaly.
If you think you may have a Keratin deficiency, talk to your doctor. They can order tests to check your Keratin levels and ensure you're getting enough Keratin in your diet.
Beef: Beef is a good source of Keratin. It's exceptionally high in Keratin if you eat it with intact bone marrow.
Chicken: Chicken is a good source of Keratin. It's incredibly high in Keratin if you eat it with intact skin.
Eggs: Eggs are a good source of Keratin. If you eat them with the shells intact, they're incredibly high in Keratin.
Dairy: Dairy products such as milk, cheese, and yogurt are good sources of Keratin.
Nuts: Nuts such as almonds and Brazil nuts are good sources of Keratin.
Soy: Soy products such as tofu and soy milk are good sources of Keratin.
Sometimes, the body overproduces Keratin. This condition is called hyperkeratosis.
There are many types of hyperkeratosis, but all involve an overgrowth of the protein keratin. This overgrowth can cause the skin to become thick, hard, and cracked. It can also lead to calluses, corns, and warts.
Several things can cause hyperkeratosis. Excess keratin production can happen due to genetic disorders, certain medications, or chemical exposure.
Poor circulation: Poor circulation can cause an accumulation of dead skin cells on the skin's surface. This accumulation can lead to hyperkeratosis.
Friction: Friction from shoes, clothing, or other objects can cause hyperkeratosis. This overgrowth often happens in people who wear ill-fitting shoes or have jobs requiring them to wear gloves.
Injury: Injury to the skin can cause hyperkeratosis. This overgrowth often happens in people who have burns or had surgery.
Certain medical conditions: Certain medical conditions, such as psoriasis and eczema, can cause hyperkeratosis.
Actinic keratosis is a condition in which patches of thick, scaly skin develop on sun-exposed areas of your body. Actinic keratosis can lead to skin cancer.
Basal cell carcinoma: This is the most common type of skin cancer. It usually appears as a small, flesh-colored bump on the sun-exposed areas of your body. Basal cell carcinoma can be disfiguring if left untreated.
Squamous cell carcinoma is the second most common type of skin cancer. It usually appears as a firm, red bump on the sun-exposed areas of your body. Squamous cell carcinoma can be disfiguring left untreated.
To diagnose hyperkeratosis, your doctor will ask about your medical history and symptoms. They may also do a physical exam.
Skin biopsy is a test in which a small piece of skin is removed and examined under a microscope. A skin biopsy can confirm the diagnosis of hyperkeratosis.
Light microscopy is a test in which a skin sample gets examined under a microscope. Light microscopy can help your doctor to rule out other conditions.
If you have hyperkeratosis, there are several treatment options available. Treatment will depend on the type of hyperkeratosis you have and how severe it is. Treatment options include:
Topical treatments: These are medications that get applied to the skin. Topical treatments can help to soften the thickened skin and reduce scaling.
Oral medications: These are medications taken by mouth. Oral medications can help to reduce inflammation and itching.
Surgery: In some cases, surgery may be necessary to remove thickened areas of skin.